
What becomes of our digital life when supercomputers are commonplace? In this situation, experts rely on a field known as quantum security. The more quantum technology that is being invented, the way we defend against sensitive information is also under examination. Encryption techniques currently in place can be made redundant within the next few years. Remaining ahead of the threat posed by supercomputing requires quantum security. This article explores how quantum security is changing the future of data protection and securing systems more than ever.
The Threat to Current Cryptographic Algorithms
Current cryptographic algorithms depend a lot on mathematical problems that it is practically impossible to break using conventional computers. Current algorithms of encryption, like RSA and ECC, depend on the assumption that factoring large numbers or solving discrete logarithms will take thousands of years. Quantum Computers destroy this assumption. These computers can execute calculations at light speed and are capable of breaking these conventional systems within seconds. Therefore, present-day encryption methods will be obsolete and extremely vulnerable very shortly.
To address these threats, quantum security has become a pressing need at once. Quantum security brings in new systems that are quantum-resistant to attacks. Quantum cybersecurity is aimed at setting up new mechanisms to encode, transmit, and decode information securely despite quantum attackers. Governments, research centers, and technology companies have begun to invest heavily in quantum cybersecurity solutions. Their rationale is straightforward: adopt future-proof security solutions in the present, before Quantum Computing can release its threat.
Introducing Post-Quantum Cryptography
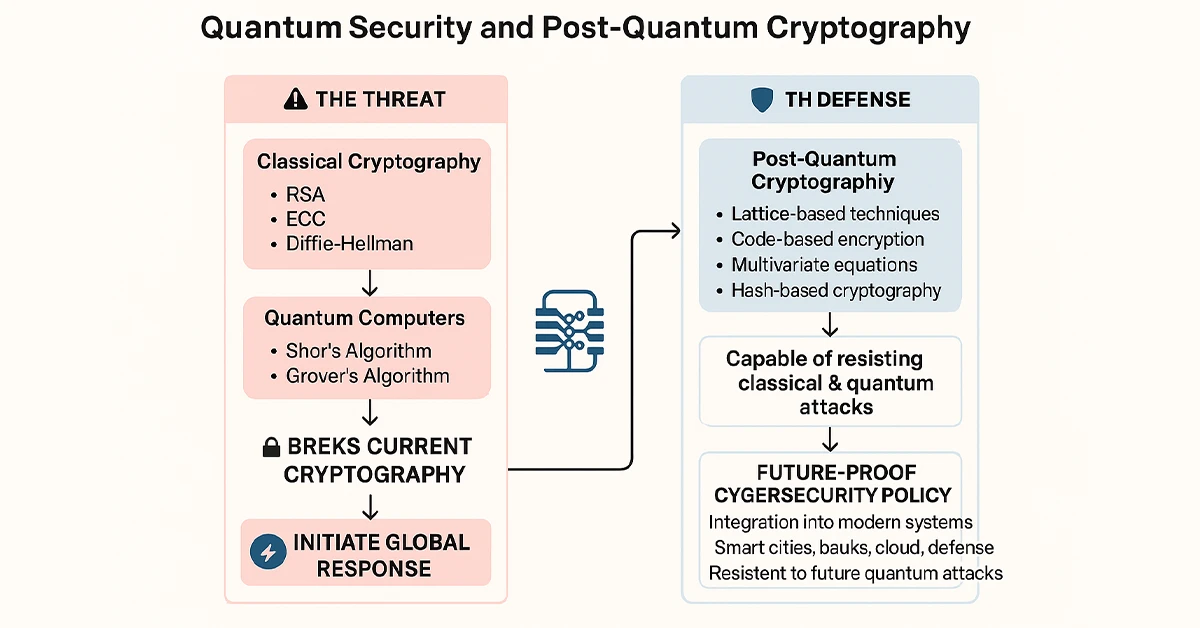
Quantum security is no longer a distant concept — it’s soon to be the foundation of global cybersecurity policy. As Quantum Computers are developing, they will make old cryptographic systems redundant. To counter this, researchers and cybersecurity professionals are working on a revolutionary method called Post-Quantum Cryptography. This discipline is all about creating encryption methods that are safe even against future quantum machines.
Unlike traditional techniques like RSA or ECC, Post-Quantum Cryptography is based on mathematical problems difficult for quantum computers to perform. These include encryption techniques based on lattices, hashes, codes, and multivariates. All these techniques provide immunity against both classical and quantum computational attacks.
Government leaders and international institutions are not taking this shift lightly. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has already started to choose and certify the best quantum security algorithms through an ongoing multi-year process. This is a full turnaround in the approach that the cybersecurity community understands protection for digital things — no longer as a dash to be the quickest but as a call for improved smarter defenses.
By integrating Post-Quantum Cryptography into the systems of today, we can create a secure digital world that can withstand even in the age of Quantum Computing.
NCOG is implementing these post-quantum concepts and creating blockchain infrastructure that is ahead of its time in terms of cryptographic security.
The Power and Risk of Quantum Computers
Compared to classical computers, quantum computers operate on completely different principles. Rather than binary bits being 0 or 1, Quantum Computers utilize quantum bits — or qubits, which exist in more than one position simultaneously because of superposition and entanglement. Quantum Computers can hence compute many calculations at the same time, solving complex problems much faster than any classical computer.
While this computer capacity brings science, medical, and artificial intelligence advancements, it also brings gigantic risks. Quantum Computers can be used by ill-intentioned parties to crack existing cryptography systems protecting everything from bank transfers to government information and personal data. Fear of cracking digital trust has fostered an extreme need for quantum security solutions.
Among the worst is the “harvest now, decrypt later” strategy. Already, encrypted data has been being gathered with intent to decrypt it when Quantum Computers are powerful enough. This pending threat puts today’s secret communications and sensitive records to risk. To prevent this, quantum security…
Comments
Post a Comment